Site Administration
Introduction
To get to the administration page for your website, you can add ‘wp-admin’ to the end of the URL. If you aren’t logged in, you’ll be asked to do so.
All content creation and management occur from the admin panel. It’s worth remembering that a CMS divides the content and the way the content is displayed. We’ll get onto styling the content, but for now, let’s look at creating content and the various types of content on WordPress.
Content types
There are three content types. Please click on the tabs below for details:
Posts When WordPress was developed, a blogging platform and ‘posts’ were the primary content created.
Posts are generally editorial – like blogs - and authors, dates and any tags the author wants to add are assigned to posts. This makes it easy for users to search through posts to find topics and posts from a specific author.
Pages Pages are typically what you’d expect from a website. Things like home pages, about pages etc. They are static and not connected to authors and dates because they don’t change, and it doesn’t matter who wrote them.
You can have child-parent relationships for pages where a page is a sub-page of another. An example could be an FAQ page that you can click on from the Contact page. Generally, a page is something that you’d find on a menu and isn’t updated often.
Media Media items like images can be uploaded and are stored on the web host, while data about the media item is stored on the database. The stored data are things like titles and alt text. Media items can be used on different pages and posts across the site.
Block editor
From v5.0 and later, WordPress rolled out an editor called Gutenberg with a unique way of creating blocks of content for the page.
Using their block editor, you can add individual blocks of content like Paragraph, Image, Gallery, Quote, List etc. into the page or post and edit it.
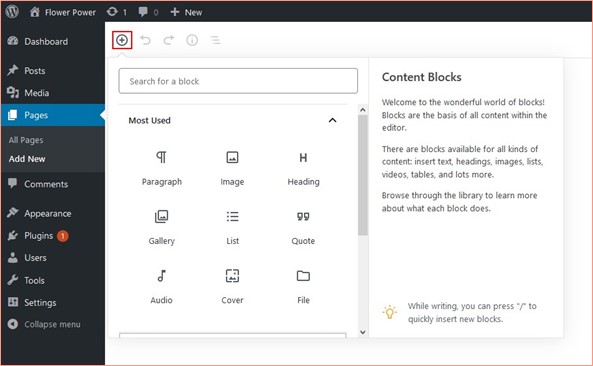
The WordPress admin panel is quite intuitive, but if you want more information about how to set up the admin panel and use all the elements correctly, you can look at the following video.
WATCH
Video: WordPress 5 Essential Training
Plugins
If you are looking for added functionality for your site beyond the standard WordPress installation, a good place to look is for a plugin.
A plugin is a piece of software written on PHP which you can download and install to your WordPress site. Using plugins can speed up the development of a project and means you can get quite a lot of functionality without needing knowledge of how it was created.
Most plugins are free with limited functionality. You pay extra for added functionality.
The following video covers content management and introduces you to the WordPress block editor.
You can watch the video further if you’re interested and want to learn more about the block editor.
WATCH
Video: WordPress 5 Essential Training 2. Content Management (11m)
Lesson Task
Brief
Create a page on the WordPress admin panel and take some time to familiarise yourself with the block editor by adding various blocks to the page. See what is available and how it works.